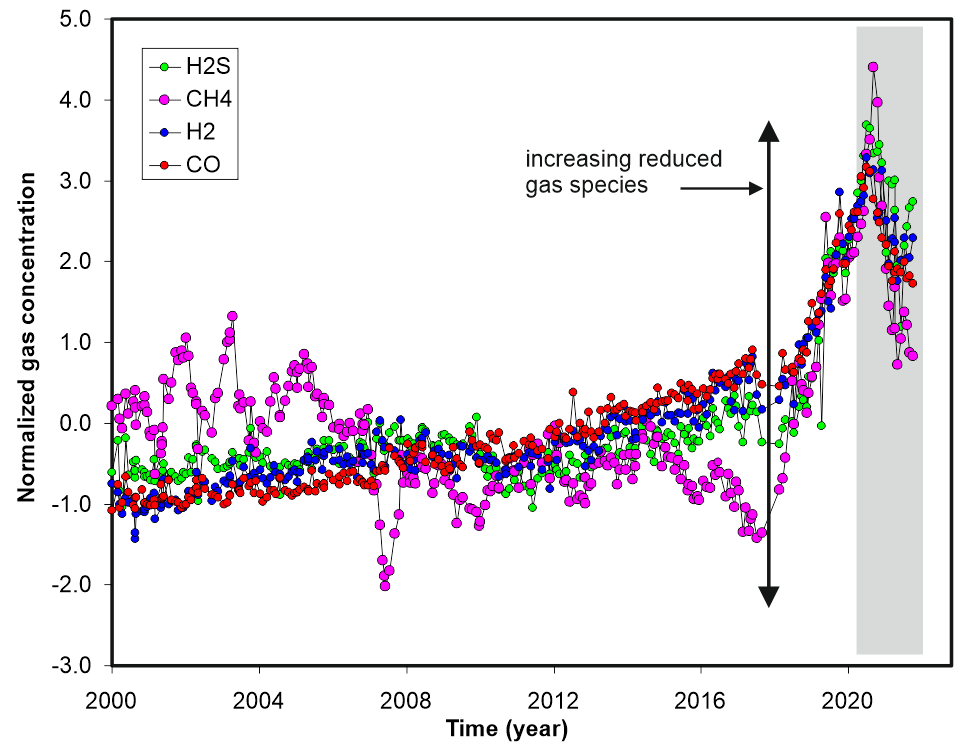
 Figure 2.1 Normalized fumarolic gas compositions post 2000.
Figure 2.1 Normalized fumarolic gas compositions post 2000.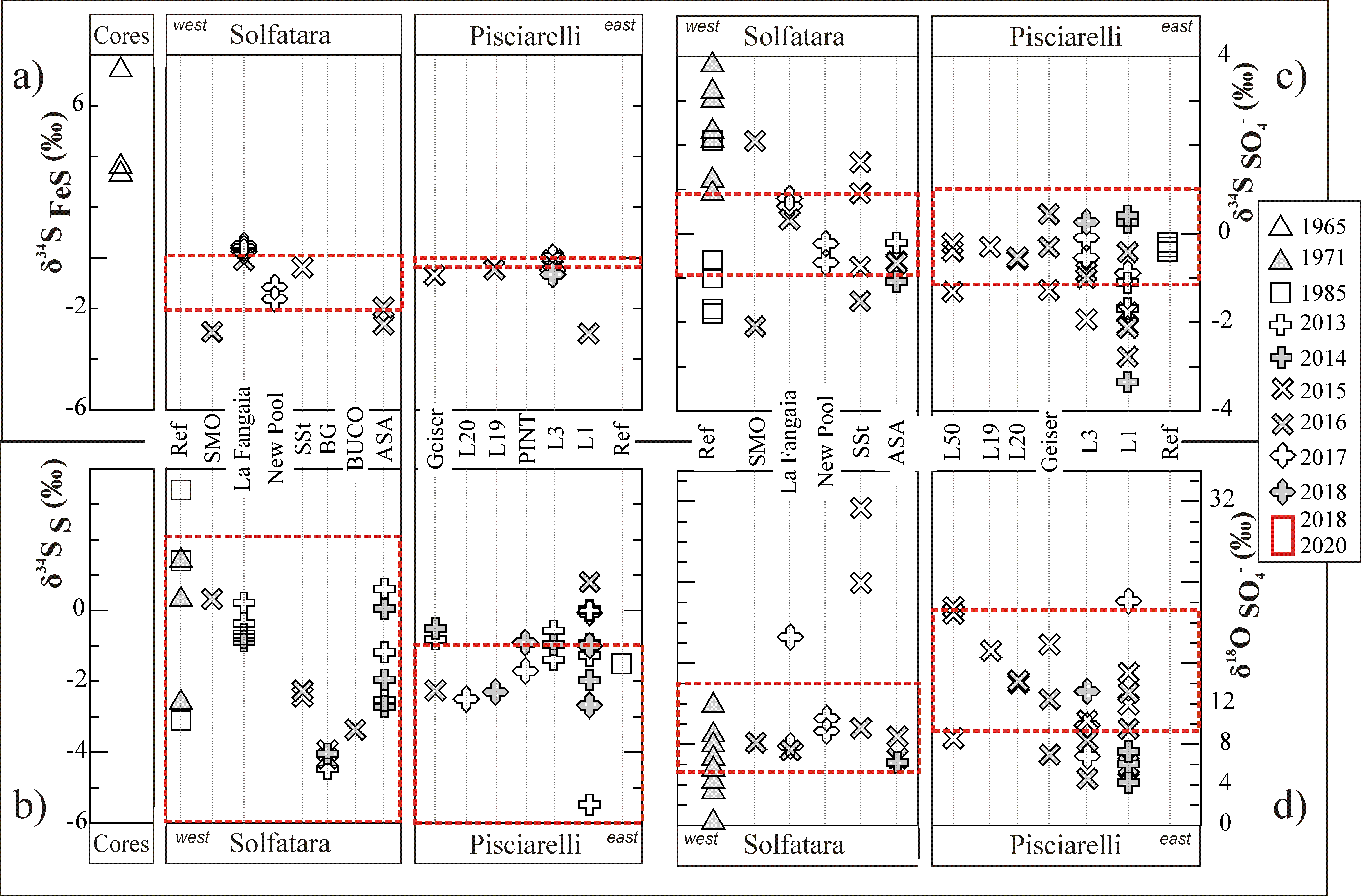 δ18O and δ34O values in various S-bearing minerals through time and at specific hydrothermal sites.
δ18O and δ34O values in various S-bearing minerals through time and at specific hydrothermal sites.This WP will deal with the dynamics of the hydrothermal system, whose knowledge is based on the large dataset of compositions of fumaroles systematically collected since the 80s and of hydrothermal mineral assemblages investigated since the 2012. The evolution and current state of the hydrothermal system are investigated by innovative geochemical measurements on fumarolic fluid and alteration rock samples collected both on land (Solfatara-Pisciarelli) and underwater (“Secca delle Fumose”) in the Gulf of Pozzuoli (task 2.1 and 2.2).
The main objectives of the WP are to understand the relationships between shallow plumbing system and magma degassing at depth, by means of the pattern of geochemical indicators and the alteration characteristics of rocks measured at the surface. Moreover, statistical analyses of geochemical records will be performed with the aim to quantitatively compare different types of multiparametric data, making efforts towards their statistical combination, and then possibly predict the approaching of rock-failure due to magma movement at depth (task 2.3).
The WP consists of three Tasks:
The Task 2.1 focus on the evolution and the current state of the hydrothermal system with particular attention to the most recent variations, i.e. the clear increase, since 2017-2018, of the concentrations of all the monitored reduced gas species (i.e. H2S, H2, CO and CH4;). This variation interrupts years of relatively oxidized conditions of the system and open important questions regarding the origin of the change and the interpretation in the frame of the Campi Flegrei surveillance.
In the frame of task 2.2, the minero-petrological features of hydrothermal alteration products and the stable isotopic compositions of sulfur-bearing minerals have been determined updating on August 2021 the already existing information (Piochi et al. 2019). This task focuses on the study of alteration products and the secondary mineralizations that mostly occur in the Solfatara-Pisciarelli site. In this area the presence of these minerals is due to the mutual transformation of rocks and infiltrating fluids under dynamic physico-chemical conditions sustained by endogenous heating reservoirs, in an attempt to reach the thermodynamic equilibrium. Planned activity included field survey with collection and multi-methodological minero-petrological investigations of the hydrothermal alteration products at the acidic sulfate setting.
Task 2.3 Planned activity concerned the collection and homogenization of the geophysical and geochemical data. The two groups of variables will be analyzed by means of Principal Component Analysis and both the relations between the groups and within the same group will be discussed. Space-time clustering will characterize sub-processes. The theory of the failure forecast method (FFM; Voight, 1989) and its probabilistic enhancement (pFFM; Bevilacqua et al., 2019), will allows the nonlinear regression and stochastic extrapolation of the failure time forecast updated to 01/01/2022.
